Home > Software >
Current release: v0.2 - Download
Release: v0.1 - Download
BoolSPL (Boolean S-box parallel library for GPU) provides, reusable software components for every layer of the CUDA programming model [5]. BoolSPLG is a library consisting procedures for analysis and compute cryptographic properties of Boolean and Vector Boolean function (S-box). Our procedures have function for auto grid configuration. Most of the functions are designed to compute the data in registers because they offer the highest bandwidth.
The proposed library implement algorithm as composition of basic function into one parameterized kernel, without care about details of implementation. The building function can be classified into computation (Butterfly (FWT, IFWT, FMT, bitwise FMT, min-max), DDT, AlgebraicDegree, ComponentFunction, PowerInt), reordering operations (Copy, MemoryPatern) and support operation reduction (min, max).
Figure 1 presents a scheme with the classification of the functions used to build procedures for computing the cryptographic properties of Boolean and Vector Boolean function. The solid line indicates a dependency while the dashed line represents an optional component.
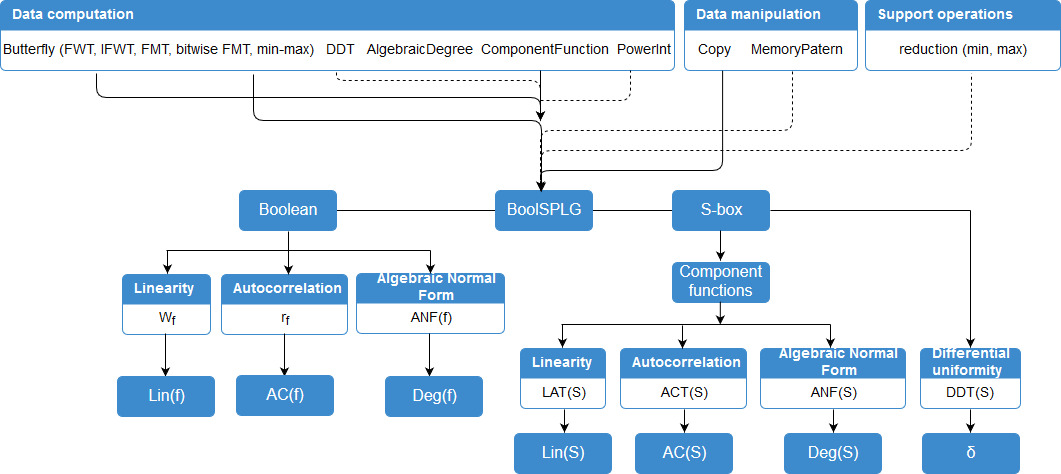
Our library contains the following butterfly algorithms: binary Fast Walsh Transforms (FWT), binary Inverse Fast Walsh Transforms (IFWT), binary Fast Mobius Transforms (FMT), Bitwise binary Fast Mobius Transform (bitwise FMT) and butterfly Min-Max. There are additional algorithms and function for computing DDT, algebraic normal form, component function and auxiliary function reduction for maintaining necessary operations figure 1.
Included procedure in BoolSPLG compute next cryptographic properties: Wf(f) (Walsh spectra of Boolean function), Lin(f) (Linearity of Boolean function), LAT(S) (Linear Approximation Table of S-box), Lin(S) (Linearity of S-box), rf(f) (Autocorrelation Spectrum of Boolean function), AC(f) (Autocorrelation of Boolean function), ACT(S) (Autocorrelation spectrum of S-box), AC(S) (Autocorrelation of S-box), ANF(f) (Algebraic Normal Form of Boolean function), ANF(S) (Algebraic Normal Form of S-box), Deg(f) (Algebraic Degree of Boolean function), Deg(S) (Algebraic Degree of S-box), DDT(S) (Difference Distribution Table), δ (Differential uniformity) and Sb (Component function of S-box) [1].
BoolSPL is implemented as a C++ header library. There is no need to “build” BoolSPL separately. To use BoolSPL primitives in your code, simply:
1. Download and unzip the latest BoolSPL distribution from the Downloads section and extract the contents of the zip file to a directory.
You need to install (copy) only “BoolSPL” directory from the main BoolSPL-vx.x directory. We suggest installing BoolSPL to the CUDA include directory,
which is usually:
- /usr/local/cuda/include/ on a Linux and Mac OSX;
- C:\CUDA\include\ on a Windows system.
Example: C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v8.0\include\;
If you are unable to install BoolSPL to the CUDA include directory, then you can place BoolSPL somewhere in your home directory,
for example: /home/nathan/libraries/.
2. #include the "umbrella"
3. Compile your program with NVIDIA's nvcc CUDA compiler, specifying a -I
BoolSPL distribution directory contain “examples” directory with examples (Boolean and S-box) programs.
For the examples to work there is need to include (add) the additional header files from the directory “help and additional header files”.
This additional header files contain CPU Boolean and S-box function used for comparison and checking the obtained results from GPU functions.
BSbox-tools is developed console application program for representation, defining and computing the most important cryptographic properties of Boolean and Vector Boolean functions (S-boxes).
With other words BSbox-tools represents a console interface program on the BoolSPL library.
The version BSbox-tools_v0.2 is based on BoolSPL_v0.2 library version. Availaible on: link
[1] D. Bikov and I. Bouyukliev, BoolSPLG: A library with parallel algorithms for Boolean functions and S-boxes for GPU, preprint.
[2] D. Bikov, I. Bouyukliev, Parallel Fast Walsh Transform Algorithm and its implementation with CUDA on GPUs. Cybernetics and Information Technologies. Cybernetics and Information Technologies 18, 21–43 (2018).
[3] D. Bikov and I. Bouyukliev, Parallel Fast Mobius (Reed-Muller) Transform and its Implementation with CUDA on GPUs, Proceedings of PASCO 2017, Kaiserslautern, Germany, Germany — July 23 - 24, 2017, ISBN: 978-1-4503-5288-8 (improvement presented in this publication are implemented in current v0.2 BoolSPL library)
[4] D. Bikov and I. Bouyukliev, BoolSPLG: A library with parallel algorithms for Boolean functions and S-boxes for GPU, Poster session, PUMPS+AI 2018, Barcelona, Spain.
[5] CUDA homepage, Availaible on: https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-zone
[1] I. Bouyukliev, D, Bikov, Applications of the binary representation of integers in algorithms for boolean functions, Proceedings of the Forty Fourth Spring Conference of the Union of Bulgarian Mathematicians SOK “Kamchia”, (2015), pp.161-166, ISSN: 1313-3330
[2] D. Bikov, I. Bouyukliev, Walsh Transform Algorithm and its Parallel Implementation with CUDA on GPUs, Proceedings of 25 YEARS FACULTY OF MATHEMATICS AND INFORMATICS, Veliko Tarnovo, Bulgaria, (2015), pp. 29-34, ISBN: 978-619-00-0419-6
[3] D. Bikov, I. Bouyukliev, A. Stojanova, Benefit of Using Shared Memory in Implementation of Parallel FWT Algorithm with CUDA C on GPUs, Proceedings of 7th International Conference Information Technologies and Education Development, Zrenjanin, Serbia, (2016) pp.250-256, ISBN 978-86-7672-285-3
[4] I. Bouyukliev, D. Bikov, S. Bouyuklieva, S-Boxes from Binary Quasi-Cyclic Codes, Electronic Notes in Discrete Mathematics Volume 57, (2017), pp. 67–72
[5] D. Bikov, I. Bouyukliev, S. Bouyuklieva, Bijective S-boxes of Different Sizes Obtained from Quasi-Cyclic Codes, submitted.